The Cathedral is located in the centre, in the heart of the ancient city, in an elevated position, close to the Royal Palace, to which it was connected by a covered street. There is a large open space on the southern front, which is now enclosed by a balustrade.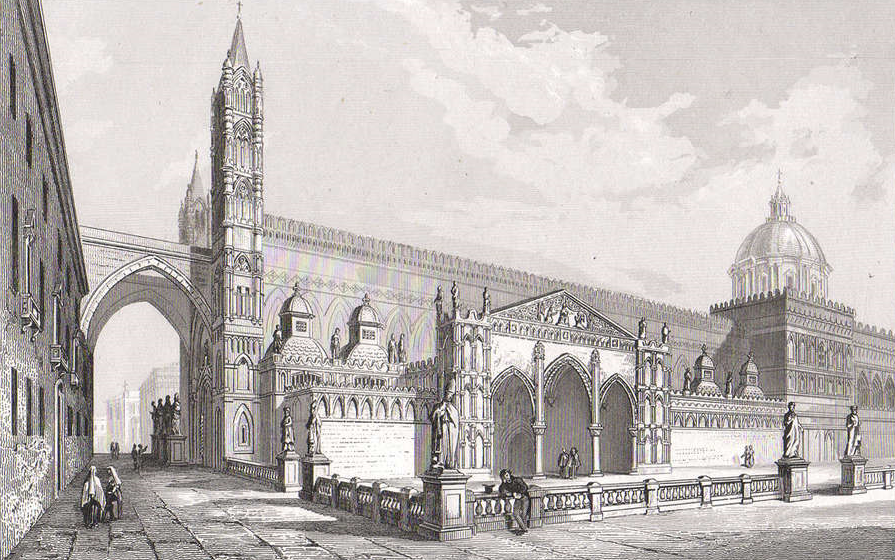
This large square is not a simple churchyard or garden, but a tangible sign of what was once Palermo’s great Friday Mosque and was intended to form the large porticoed courtyard adjacent to it.
This was, in fact, an atrium, originally enclosed on three sides by high walls, surrounded by porticoed arches and with two fountains in the centre. Until the middle of the 16th century, the
fair of Santa Cristina
was held there. In the 16th century, when the decision was made to demolish the walls and create an open space, bordered by an elegant balustrade, the two fountains which are still visible today, which are probably the remains of the fountains for the ablutions of the faithful in the ancient Mosque, were kept as a memorial.
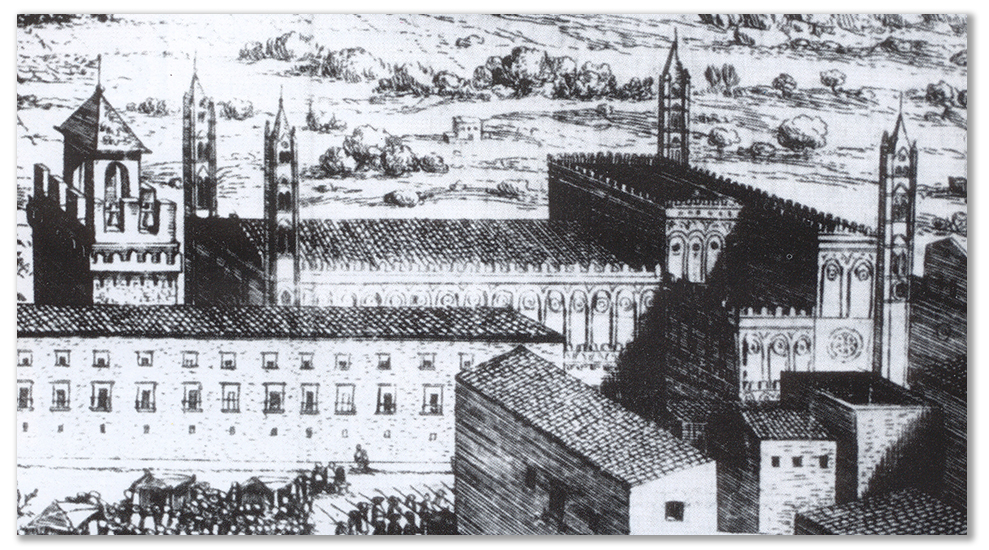
This is supported by the anomalous position of Palermo Cathedral, which is not canonically oriented on the west-east axis towards the apse, but on the south-west-north-east axis, where its façade, which faces south, is actually directed towards
Mecca
.
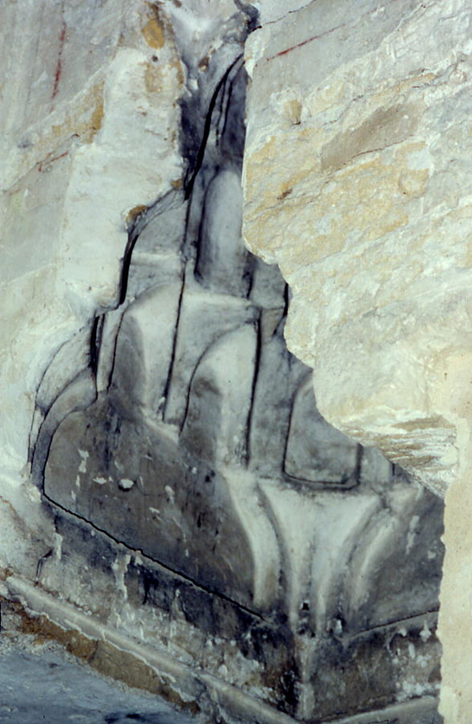
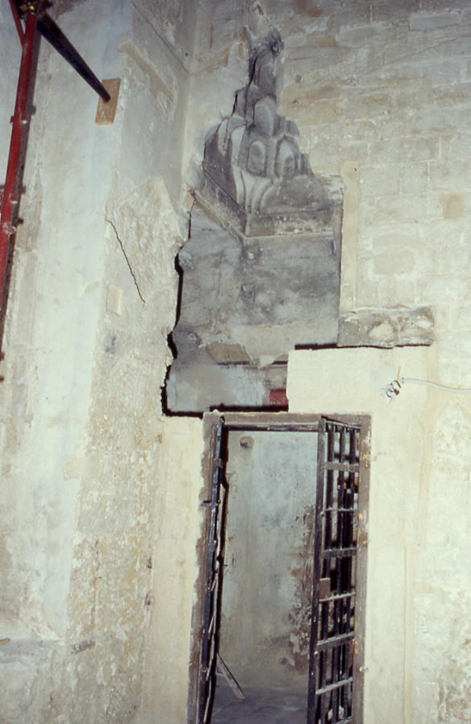


Inside the church, on this façade, recent restorations have unearthed one of the probable seven
al-mihrab
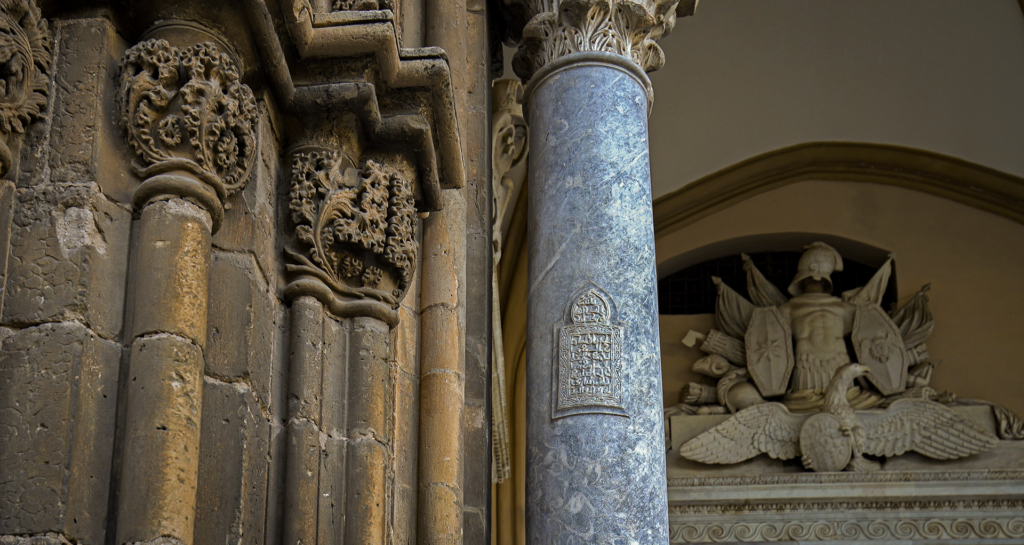
indicating the direction of Mecca. Other parts of the ancient Mosque were found, and reused in the renovation of the Cathedral, as was the custom of the time, as witnessed by a column in the southern portico, which has a verse from the
Surah of the Qur’an
.
 Today’s cathedral has undergone many changes over the years, especially at the end of the 18th century, when the architect
Ferdinando Fuga
Today’s cathedral has undergone many changes over the years, especially at the end of the 18th century, when the architect
Ferdinando Fuga
completely altered the style of the cathedral, both inside to conform to the new taste of the neoclassical style and outside with additions and modifications, including the massive transept, the large dome and the small domes.
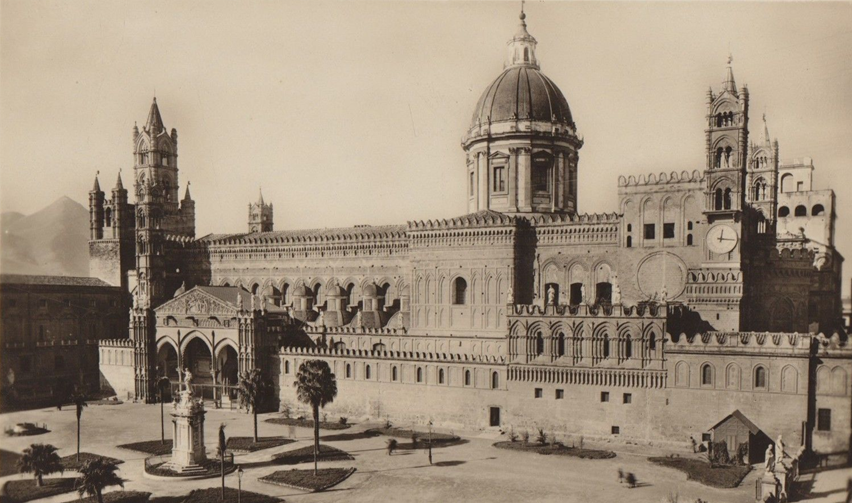 These changes have made the Palermo Cathedral an admirable palimpsest. Its beauty lies in the various stylistic overlaps, which make it a unique work of art. In its stones, where the evolution of time can be read, the history of this very happy city is engraved.
These changes have made the Palermo Cathedral an admirable palimpsest. Its beauty lies in the various stylistic overlaps, which make it a unique work of art. In its stones, where the evolution of time can be read, the history of this very happy city is engraved.