On the southern façade of the Cathedral, there is an old access to the church, through the large external floor, adjacent to it.
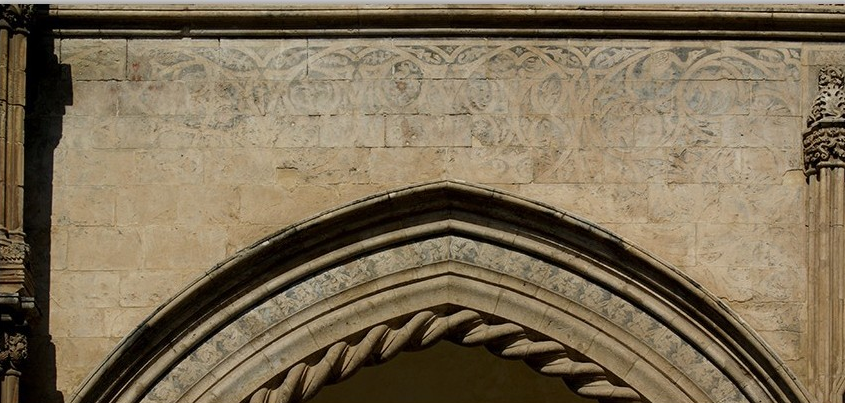

 In a little-known passage of the Latin text, the
chronicles
In a little-known passage of the Latin text, the
chronicles
report the presence of an entrance archway on the southern façade, which existed before the present one since the times of the first cathedral, enlarged by the
Great Count Roger
, then rebuilt or more probably restored by
Bishop Gualtiero
in 1185 and finally restored again in 1296, when
Frederick II of Aragon
donated the tiles of the Kingdom of Sicily.
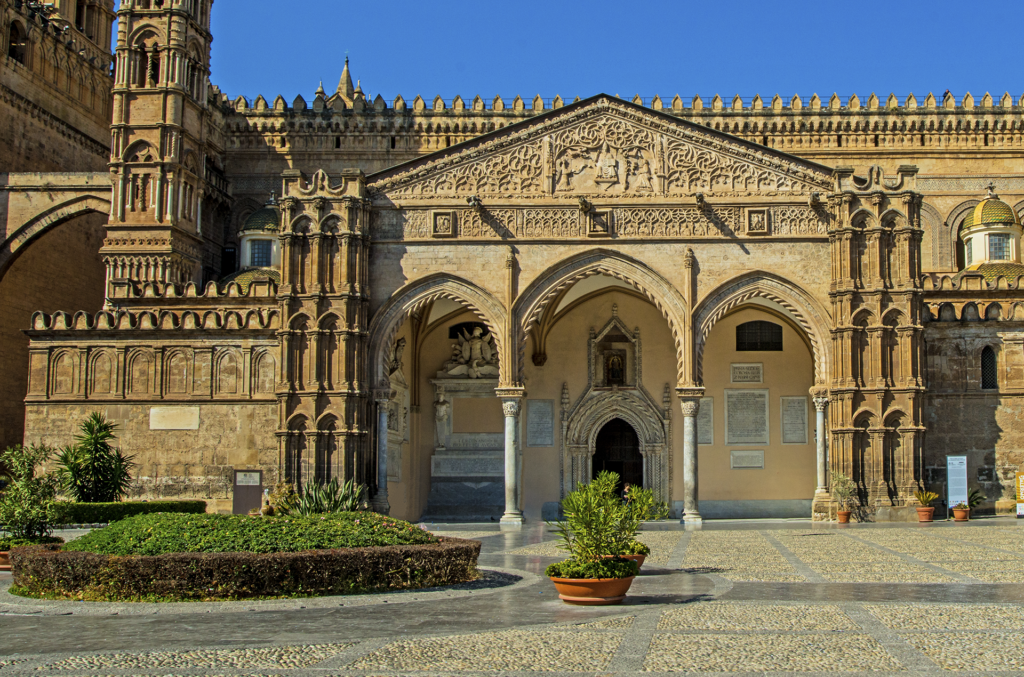

The
present portico
, in
Catalan Gothic style
, is the work of
Magister Marammae
Antonio Gambara, commissioned by the Bishop of the time,
Ubertino De Marinis
, in 1429.
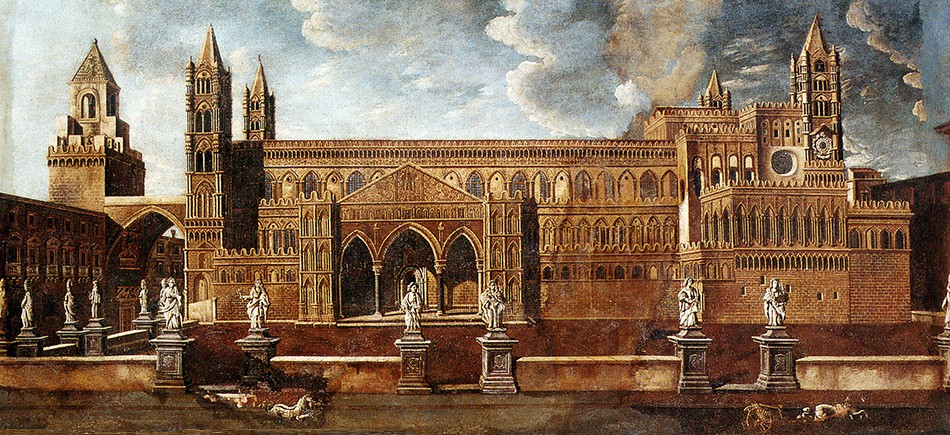
Although it is true that the construction of the southern portico of the Cathedral dates back to 1429, the studies carried out during the
last restorations
have confirmed what is reported in the chronicles that, before the present one, there was already another portico on the same side of the Cathedral. It seems plausible, therefore, that in order to carry out his valuable work, according to the style of the time, defined as the “tocco del piano” (touch of the floor),
Gambara
used and reassembled, in a valuable fusion,
some elements of artistic workmanship
, extraneous to the general composition of the portico which, when reused, show their origin from the recovery of the previous structure.