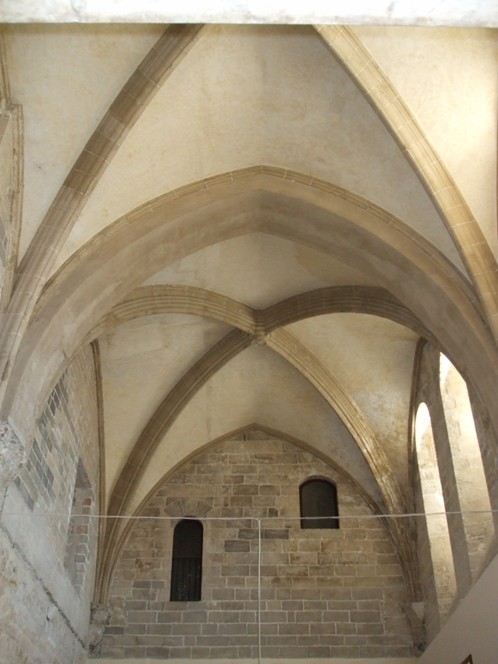
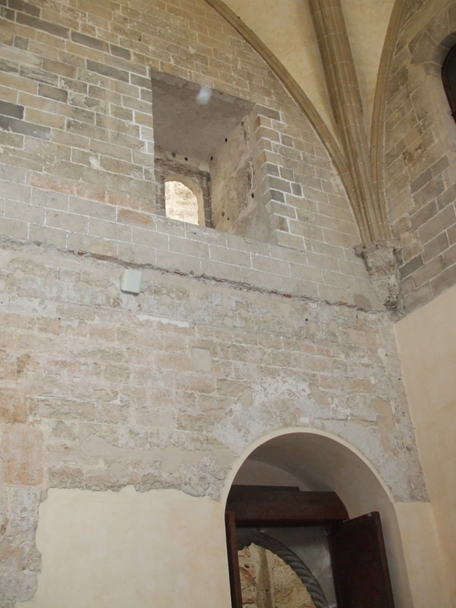
It was only after recent studies carried out in connection to the restoration work performed in Palermo Cathedral since the 1980s that the Magdalene Chapel was identified in the exact place where it was built, next to the wall of the mother church, as reported in Gualtiero’s petition. It is, therefore, identifiable in the lower part of the Old Sacristy, whose external cornice decoration is the same in the first and second orders of the scalar towers, which date back to medieval times.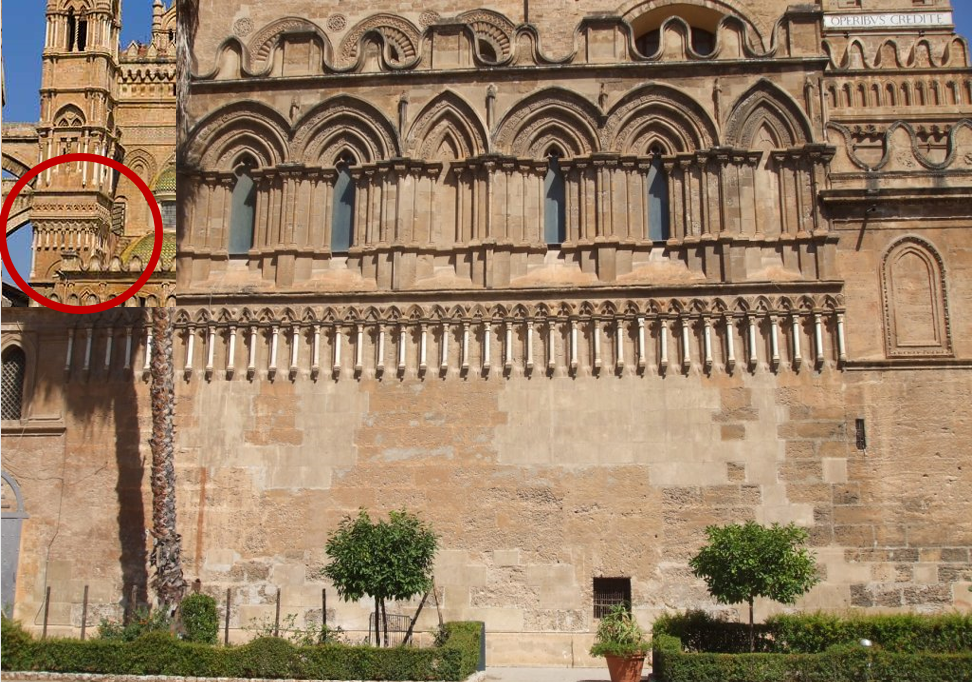
The interior of the building shows the difference between the two overlapping buildings. The part erected in the 15th century, with ribbed vaults covering the room, had also partially concealed two large single-lancet windows,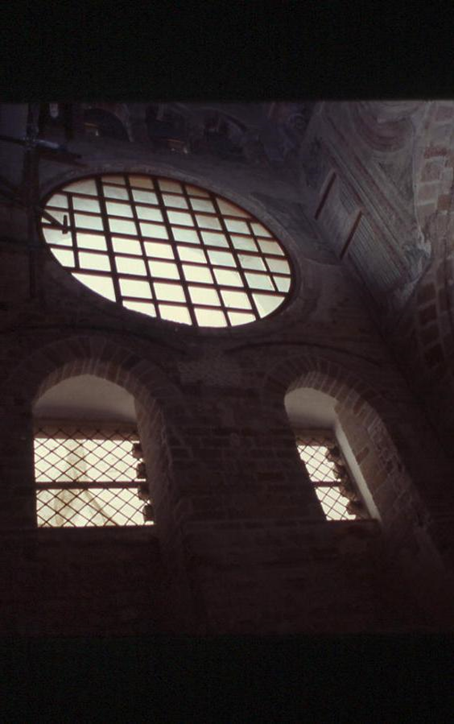  which provided light to the inside of the
Antititulo
which provided light to the inside of the
Antititulo
, close to the
apse of the Diaconico
.
The building is raised by about one metre from the external level. Underneath, there is a crypt with several chambers and a rectangular hatch in the vault, indicating its use as a burial place, according to its original purpose. The chapel, built at the behest of Queen Elvira, uncovered another interesting detail, namely a small compartment in the masonry connecting the chapel to the apse of the Diaconico.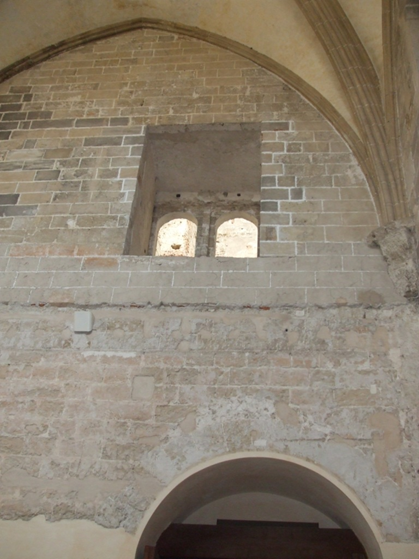
This room, which is similar to the contemporary one in Cefalù Cathedral, was probably the Queen’s gallery, where she could attend the sacred functions without being present in the presbytery area itself. The room, about 5 metres high, could be accessed via a wooden balcony, which has now been removed. It was connected to an opening in the eastern wall, which belonged to the original chapel and could be reached by a spiral staircase, which also gave access to the crypt below.
